Miniature Bearings Australia
09074 - Datasheet
MBA
Category Information
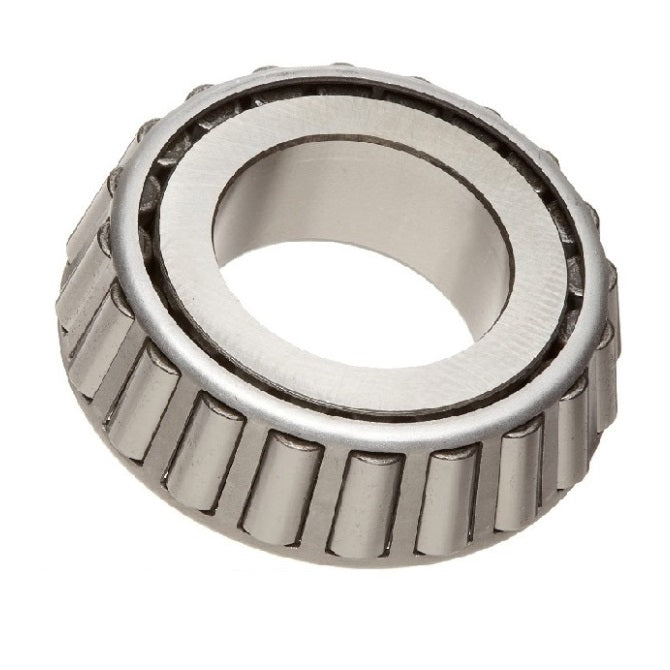
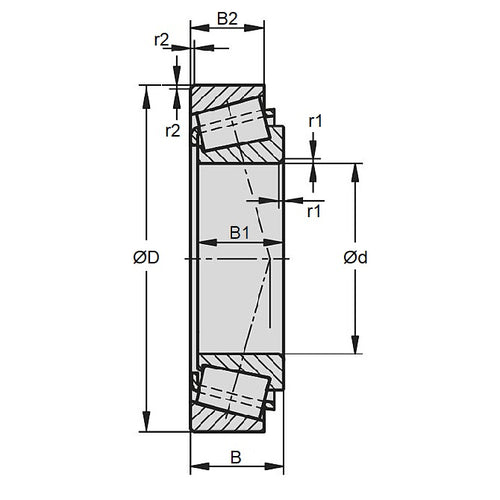
Bearings - Tapered Roller ConeTapered Roller Cone Bearings. Replacements for existing tapered roller cones (inner part). Match with part number on your existing bearing. It is recommended that you change both cup and cone whenever possible.
- Tapered roller bearings provide for high thrust and axial loads, and are commonly used in automotive applications such as wheels, differentials and gearboxes.
- Match the cone with the appropriate cup as listed in the tables. Sometimes there will be a range of cups to suit. Be sure to check the dimesions thoroughly.
- The cup is the outer part of the bearing, and has no rollers. An expanded range may be available on special order. Please enquire.
Product Data
- Inside Diameter
:
19.050
mm
(Equiv. 0.75 in.) - Cone Width
19.050
mm
(Equiv. 0.75 in.) - Matching Cups 09194, 09195, 09196
- rs1 min 1.300 mm
- rs2 min 1.300 mm
- Basic Dynamic Load Rating 37500 Cr (N)
- Basic Static Load Rating 37500 Cor (N)
- Limiting Speed with Grease 8500 RPM
- Material Chrome Steel
Product Compliance and Data
Additional Resources
- Catalogue: Ceramic Bearings Catalogue
- Catalogue: Plastic Bearings Catalogue
- Catalogue: Standard Bearings Catalogue
- General: Bearing Cleanliness
- General: Bearing Clearances
- General: Bearing Flanges & Snap Rings
- General: Bearing Retainers (Cages)
- General: General Loads Information
- General: Lubrication
- General: Prefix & Suffix Guide
- General: Static vs Dynamic Loads
- Materials: 316 Stainless
- Materials: CASSTOP Anti-Corrosion Bearing Material
- Materials: Ceramic vs Ceramic Hybrid
- Materials: Ceramic Bearings in Vibratory Applications
- Materials: Ceramic Hybrid Bearings in Vibratory Applications
- Materials: General Bearing Materials
- Materials: Magnetism & Bearings
- Precision: 316 Stainless & Plastic Bearing Tolerances
- Precision: ABEC Basic Information
- Precision: Precision Bearing Tolerances
- Problem Solving: Bearing Failure
- Problem Solving: Fatigue (L10 Life)
- Problem Solving: Noise